Vaccines against the Mpox virus? What we know so far
The World Health Organization (WHO) has declared a rapidly spreading MPOX outbreak caused by a new dominant “clade” in Africa a global public health emergency.
This decision comes after a new strain of the virus, known as “Clade 1b”, emerged as the dominant strain in the Democratic Republic (DR) of Congo, infecting about 15,000 people and causing over 540 deaths since January 2024.
WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus expressed concern about the emergence of the virus in neighboring countries and the possibility of further spread.
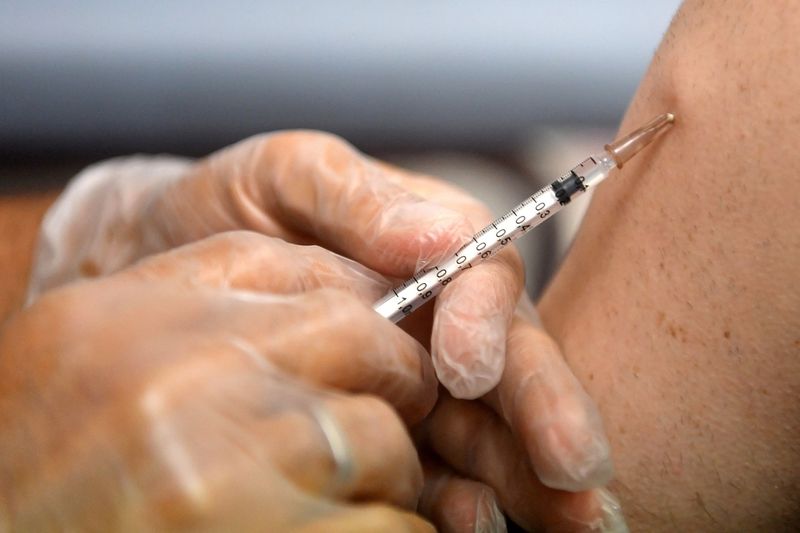
Vaccines originally developed against smallpox, including Imvanex/Imvamune and ACAM2000, are now being used to combat monkeypox, especially following the global increase in cases since May 2022.
Photo credit: AFP
WHO is urging international cooperation to counter this health threat.

Photo credit: WHO | CDC | Gulf News
How many confirmed MPOX cases and deaths are there?
Since the beginning of the year, over 15,000 cases and 548 deaths have been reported, affecting all provinces of the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Are there any confirmed Mpox cases outside Africa?
Health authorities in Sweden confirmed the first case of the more dangerous clade of the Mpox strain in August this year, marking the first time this variant has been detected outside Africa.
The patient recently traveled to a region of Africa where a significant MPOX outbreak occurred.
Olivia Wigzell, acting head of the Swedish Health Agency, told the BBC that the infected person had received treatment in the Stockholm area, but assured that treatment in Sweden would not pose a risk to the wider population.
“The person became infected while in an African region with a significant Mpox clade 1 outbreak,” Wigzell said during a press conference.
What is mpox?
Mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, spreads through close contact, including sexual contact, skin-to-skin contact, and even talking or breathing in close proximity.
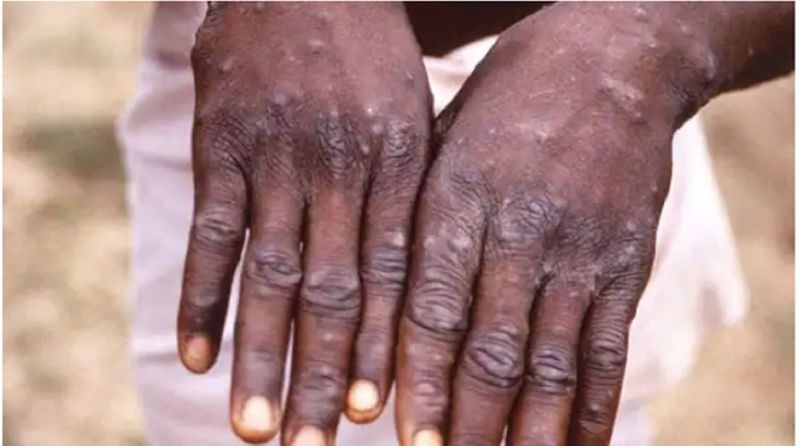
Mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, spreads through close contact, including sexual contact, skin-to-skin contact, and even talking or breathing in close proximity.
Where was the first outbreak reported?
The first outbreak was reported in the Democratic Republic of Congo, where over 540 people died; since then the disease has spread to Central and East Africa.
The disease is most common in the tropical rainforests of West and Central Africa, where thousands of infections occur each year.
What are the symptoms?
Mpox can cause serious illness and is usually manifested by the following symptoms:
- Flu-like symptoms
- Skin lesions
- Fever
- rash
In severe cases it can lead to death.
What is the mortality rate?
Most people survive an Mpox infection, but the disease can be fatal. According to the WHO, the mortality rate is four out of 100 cases.
Monkeypox vs. Mpox: What’s the Difference?
• There is no difference between monkeypox and MPOX.
• The term “Mpox” is a newer name for the disease that was previously called “monkeypox.”
• The name was changed to avoid confusion and stigma associated with the original name.
What are the main concerns with Mpox infections?
- Highly contagious and deadly variant: The new Mpox variant is more contagious and leads to higher death rates.
- High mortality rate: The Mpox strain circulating in the Democratic Republic of Congo, clade 1b, is more deadly than the previously dominant clade 2b.
- Limited resources: Due to limited healthcare infrastructure and resources, the country faces challenges in controlling the outbreak.
- Complex environment: Ongoing conflict and displacement within the country hamper health efforts.
- Vaccination efforts: Although the United States has pledged to donate 50,000 vaccine doses, overall vaccination rates remain low.
The government of the Democratic Republic of Congo is responding with increased surveillance, awareness campaigns and contact tracing. However, the situation remains critical and requires urgent international support to contain the outbreak.
How high is the risk of infection?
Although the WHO has declared the MPOX outbreak centered in the Democratic Republic of Congo a global health emergency, the risk to the population as a whole remains low.
However, the WHO warns of possible imported cases to Europe. It also advises against stigmatizing travelers.
How deadly is the latest Mpox strain?
The 2024 MPOX strain is considered more deadly, which is why the WHO pulled the trigger relatively early in the outbreak.
Who is at risk?
The risk of hospital treatment is higher in:
- Older people
- Small children
- People with a disease or who are taking a medication that affects their immune system
Are there vaccines against the Mpox virus?
There are vaccines to protect against Mpox.
Vaccines originally developed against smallpox, including Imvanex/Imvamune and ACAM2000, are now being used to combat monkeypox, especially following the global increase in cases since May 2022.
The vaccines have a favorable safety profile and most side effects are mild.
What to do if you suspect you have been infected with Mpox?
- Report to the nearest health facility
- If your symptoms are mild, you may be asked to isolate at home.
- Mpox is usually mild and most people recover within a few weeks without treatment.
- However, if your symptoms are more severe and you feel unwell, you may need hospital treatment.

